Gear Pumps for Work Trucks - How to Choose the Right One
Gear pumps are a type of displacement pump and are used in pumping fluids such as motor oil and liquid fuels. They are used to pump high-viscosity fluids in several different applications including paints, chemicals, food products like corn syrup or chocolate, soaps, and of course, various fuel and lube oils. There are two types of gear pumps: internal and external.
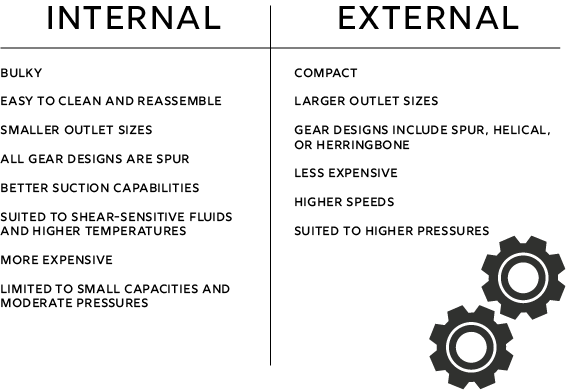
Internal Gear Pumps
Internal pumps operate with two different-sized gears with the smaller rotating inside the larger. Internal pumps are great for thicker fluids and high temperatures. Internal pumps specialize in pumping resins, asphalt and tar, food products, paints, and more. These pumps can also pump fuel and lube oils.
External Gear Pumps
External pumps have two identical gears with one gear driven by a motor and consequently driving the other gear. They are used to transfer liquids such as gasoline, diesel, and kerosene, and in applications such as elevators and chemical mixing (Pumps & Systems). External pumps are “particularly useful to provide power in areas where electrical equipment is bulky… Tractors, for example, rely on engine-driven external gear pumps to power their services” (Michael Smith Engineers LTD).
Choosing a Gear Pump - Questions to Ask Yourself
Before choosing which gear pump is right for you and your application, consider the following questions to ensure you make the right decision:
· What fluid are you pumping? What is the consistency and temperature of the fluid?
· Does your application require accurate dosing and/or high-pressure output?
· Does your application take hygiene into consideration?
· What speed does your fluid need to be pumped?
Gear Pump Common Problems & Maintenance - Other Things to Consider
Gear pumps perform at their best when the gears are wetted and lubricated. These pumps should not run dry for long periods of time.
You are likely to experience more wear if you are pumping abrasive or solid-containing fluids. As a protective measure, it is recommended you install a strainer on the suction side of the pump.
Once a gear pump has worn down, there will be an increase in “flow slip.” This means the pumped fluid will leak and can decrease performance.
Choosing a Gear Pump
Do further research to ensure you are purchasing the right gear pump for your application, and that you’ll know how to handle any problems that may arise. Remember to refer back to the list questions when determining which pump might be the perfect fit.